Suspected cases of monkeypox are under investigation in the Montreal area as more reports of infections of the rare disease are popping up globally in recent weeks.
At least seven suspected cases have been detected in Montreal, according to Dr. Donald Vinh, an infectious disease specialist and medical microbiologist at the McGill University Health Centre.
Montreal's public health department did not respond to questions from CTV News late Wednesday afternoon, but did confirm there will be a news conference Thursday to provide more details.
All of the cases in Montreal, which are still being analyzed, were from patients who were recently tested at clinics specializing in sexually-transmitted or blood-borne infections, according to a report by Radio-Canada.
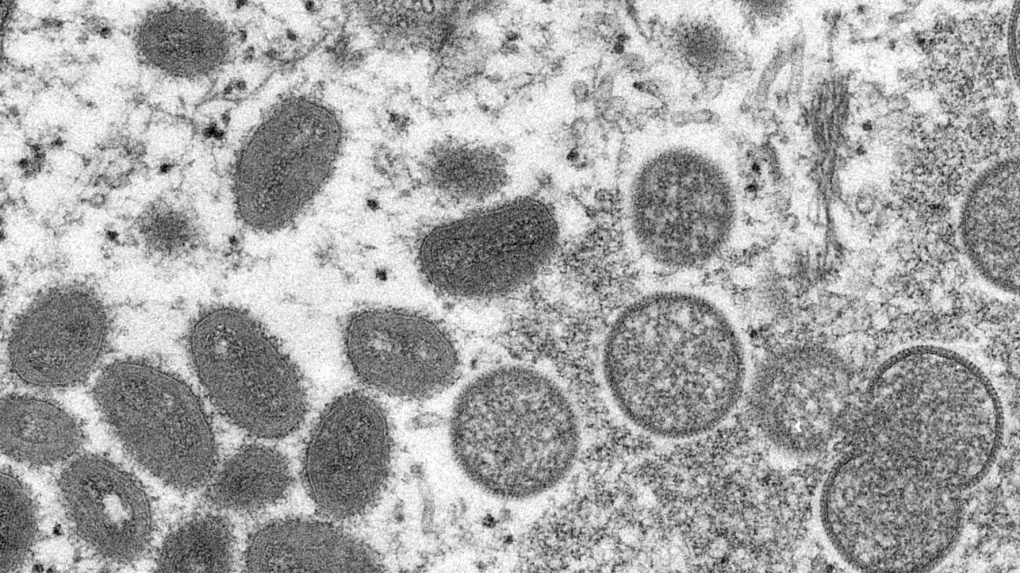
Monkeypox is a rare illness that can start to show up with symptoms like fever, headache, and fatigue. After a few days, patients can develop a rash that often starts on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body. Most patients recover in a matter of weeks, although it can be potentially fatal in some cases.
A distinguishing feature of monkeypox, compared to smallpox, is that it causes the lymph nodes to swell, according to the CDC.
On Wednesday, the Massachusetts public health department said in a statement it had confirmed one case of the disease in an adult man "with recent travel to Canada."
Marjorie Larouche, a spokesperson for Quebec's Ministry of Health and Social Services, said Wednesday evening in a statement to CTV that provincial health officials were made aware of a person infected with monkeypox who "had travelled to Quebec."
Larouche said the ministry is in contact with the Public Health Agency of Canada and that while there are no confirmed cases of monkeypox in Quebec, the ministry is "investigating approximately 10 cases of genital ulcer lesions."
"We have no further information to give at this time."
The discovery in Quebec comes after five cases have been identified in Portugal. One case was confirmed in the U.K. on May 7 and at least six more have been found since then. Spain is also monitoring 23 suspected cases.
Monkeypox was first discovered in 1958 in colonies of monkeys that were kept for research. The first human case was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, according to the CDC.