Doctors on Quebec monkeypox frontline: 'I had never heard of this disease 24 hours ago'
Health-care professionals at the forefront of containing monkeypox’s possible arrival in Montreal say it’s too early to know just how far the virus has spread.
A handful of potentially-infected patients have come to l’Actuel Clinic seeking treatment, said the centre's founder Dr. Réjean Thomas. It could take days to confirm whether they have the virus, which is difficult to diagnose on the spot.
Thomas said his staff is an unlikely first line of defence against a virus in the same family as variola, which causes smallpox. That’s because l’Actuel is a clinic that treats sexually transmitted infections.
“I had never heard of this disease 24 hours ago,” said Thomas. “The nurse told me ‘we didn’t have any education’.”
A closer look at common symptoms (which can be unsightly) does explain why people have been seeking answers for their newly-emerged illness at l’Actuel.
Thomas says the first person suspected to be positive arrived at his clinic with symptoms similar to those associated with syphilis, which creates rashes on the palms and feet. Thursday evening, Quebec's health ministry confirmed the province's first two cases of the disease and said 20 other suspected cases are under investigation.
Monkeypox symptoms, as they presented on this patient, “are on the legs and more generally [spread out],” he said.
Monkeypox, which is not an STI, can be spread through sex or any activity that includes close contact with others. Symptoms can also include swollen lymph nodes, rashes elsewhere on the body, as well as fever, headache, and exhaustion.
The virus enters the body through broken skin, the respiratory tract, or through the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Since the beginning of May, a handful of potentially-infected people have visited his clinic. For each of them, approaching a diagnosis has been a challenge.
“It can look like syphilis, it can look like herpes, it’s very difficult to diagnose,” said Thomas.
It’s also too early to determine where those possible cases came from. Thomas said some of his patients have been travelling, others have not. Some have multiple sexual partners, others do not.
Thankfully, all the suspected cases are quite mild, he said. There’s also little risk of spread among staff, who still follow strict COVID-19 preventative measures.
FEAR OF STIGMATIZATION
Thomas said the health of his patients isn’t the only thing on his mind. L’Actuel is in Montreal’s Gay Village, and many of his patients are members of the LGBTQ2S+ community.
“They're quite stressed about that disease,” he said. “They're quite worried about the stigmatization that will happen.”
Those believed to have contracted the illness in Montreal are mainly men between the ages of 30 and 55 who have had sex with other men.
Everyone is at risk of catching monkeypox, but Thomas said he’s nervous that if it continues to spread, it could fuel homophobic misinformation.
“I was there at the beginning of AIDS,” he continued. “I remember we were learning with the patients … we had no knowledge at that moment.”
He’s not the only one concerned about stigmatization.
“Just because it happened to gay men, doesn’t mean it can’t happen to heterosexual [people],” said Dr. Robert Pilarski. He specializes in STIs at La Licorne Clinic, where other potential monkeypox cases have been recorded. “It is not a gay disease; anyone can get it.”
“We do not want to stigmatize any sector of the population,” said Montreal Public Health physician Dr. Genevieve Bergeron during a Thursday morning press conference.
“What we are worried about is prolonged close contact, [which] could happen in any sort of setting.”
CTVNews.ca Top Stories
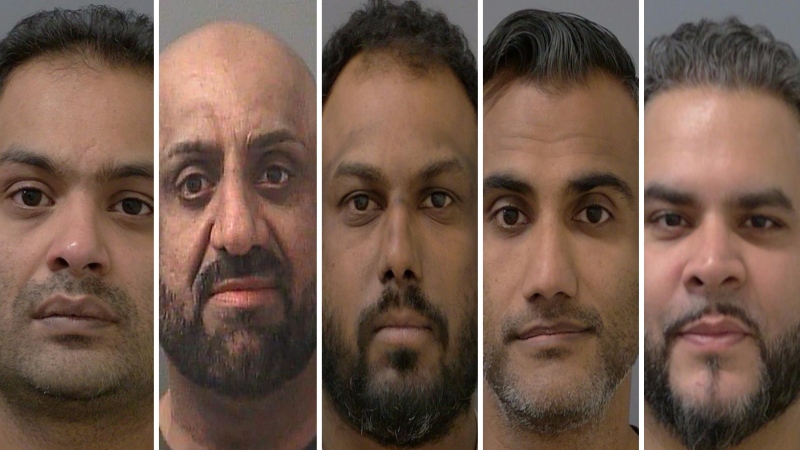

'They needed people inside Air Canada:' Police announce arrests in Pearson gold heist
Police say one former and one current employee of Air Canada are among the nine suspects that are facing charges in connection with the gold heist at Pearson International Airport last year.
House admonishes ArriveCan contractor in rare parliamentary show of power
MPs enacted an extraordinary, rarely used parliamentary power on Wednesday, summonsing an ArriveCan contractor to appear before the House of Commons where he was admonished publicly and forced to provide answers to the questions MPs said he'd previously evaded.
Leafs star Auston Matthews finishes season with 69 goals
Auston Matthews won't be joining the NHL's 70-goal club this season.
Trump lawyers say Stormy Daniels refused subpoena outside a Brooklyn bar, papers left 'at her feet'
Donald Trump's legal team says it tried serving Stormy Daniels a subpoena as she arrived for an event at a bar in Brooklyn last month, but the porn actor, who is expected to be a witness at the former president's criminal trial, refused to take it and walked away.
Why drivers in Eastern Canada could see big gas price spikes, and other Canadians won't
Drivers in Eastern Canada face a big increase in gas prices because of various factors, especially the higher cost of the summer blend, industry analysts say.
Doug Ford calls on Ontario Speaker to reverse Queen's Park keffiyeh ban
Ontario Premier Doug Ford is calling on Speaker Ted Arnott to reverse a ban on keffiyehs at Queen's Park, describing the move as “needlessly” divisive.
'A living nightmare': Winnipeg woman sentenced following campaign of harassment against man after online date
A Winnipeg woman was sentenced to house arrest after a single date with a man she met online culminated in her harassing him for years, and spurred false allegations which resulted in the innocent man being arrested three times.
Woman who pressured boyfriend to kill his ex in 2000s granted absences from prison
A woman who pressured her boyfriend into killing his teenage ex more than a decade ago will be allowed to leave prison for weeks at a time.
Customers disappointed after email listing $60K Tim Hortons prize sent in error
Several Tim Horton’s customers are feeling great disappointment after being told by the company that an email stating they won a boat worth nearly $60,000 was sent in error.